上一章粗略地对 Micronaut 了解之后,我们现在开始上手写写代码吧。
Micronaut开发环境搭建
1. 环境要求
最新版本要求JDK 17或更高版本
构建工具:Gradle或Maven
可选:Micronaut CLI(方便项目生成)
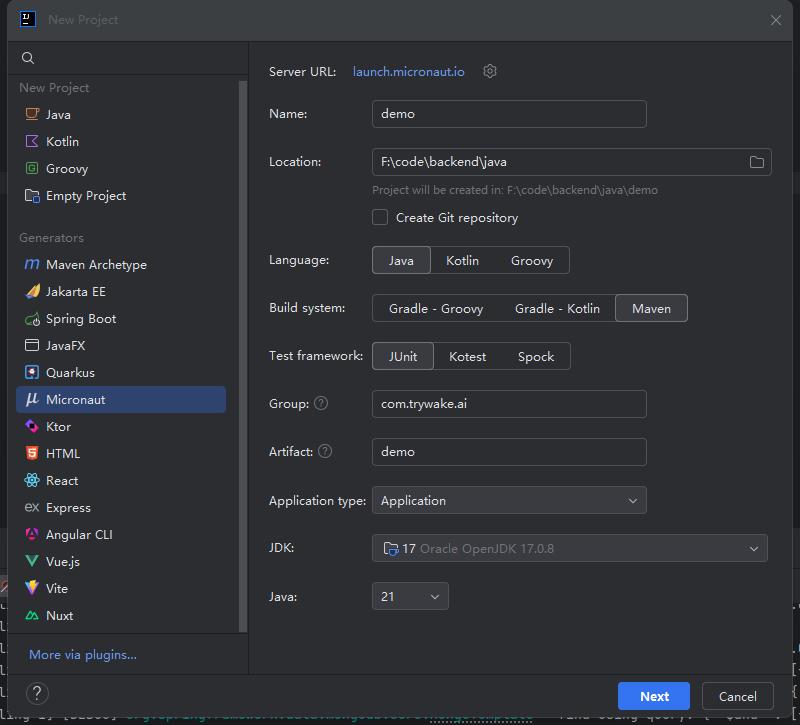
2. 创建项目
有几种方式可以创建Micronaut项目:
使用Micronaut Launch(在线向导):
访问 https://micronaut.io/launch ,选择应用类型和特性,生成项目并下载或使用CLI工具命令行参数生成项目。
使用CLI工具:
使用 sdkman 安装Micronaut CLI后运行:
mn create-app --build=gradle --jdk=17 --lang=java --test=junit com.example.demo
# 或
mn create-app --build=maven --jdk=17 --lang=java --test=junit com.example.demo使用curl直接调用API:
curl --location --request GET 'https://launch.micronaut.io/create/default/com.example.demo?lang=JAVA&build=MAVEN&test=JUNIT&javaVersion=JDK_17' --output demo.zip3. IDE支持
主流IDE都对Micronaut提供了良好支持:
IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate:提供项目向导、配置自动完成、Micronaut数据支持等
VS Code:通过GraalVM扩展包支持Micronaut开发
Eclipse:需要显式启用注解处理(APT)支持
构建Micronaut应用实践
1. 项目结构
新创建的Micronaut项目遵循标准Maven/Gradle项目结构:
src/
main/
java/ # Java源代码
resources/ # 资源文件
application.yml # 主配置文件
logback.xml # 日志配置
test/
java/ # 测试代码主应用类位于src/main/java中,通常如下(一股SpringBoot风~_~):
package com.cxl;
import io.micronaut.runtime.Micronaut;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Micronaut.run(Application.class, args);
}
}2. 开发REST API
Micronaut支持多种服务器端工作负载,包括REST、gRPC、GraphQL等。以下是开发REST API的关键步骤:
创建控制器:
package com.cxl.controller;
import io.micronaut.http.MediaType;
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Controller;
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Get;
@Controller("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@Get(uri="/{name}", produces=MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
String hello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
}这个控制器处理对/hello/{name}的GET请求,返回纯文本响应。启动应用后,可以通过curl或直接浏览器测试:
curl http://localhost:8080/hello/cxl
返回JSON响应:
package com.cxl.controller;
import io.micronaut.http.MediaType;
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Controller;
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Get;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller("/simple")
public class SimpleController {
@Get(produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Map<String, String> index() {
Map<String, String> msg = new HashMap<>();
msg.put("message", "A simple message");
return msg;
}
}3. 添加服务层
Micronaut支持分层架构,我们可以添加服务层:
// 接口定义
package com.cxl.service;
public interface IGreetingService {
String getGreeting();
}
// 实现类
package com.cxl.service.impl;
import com.cxl.service.IGreetingService;
import jakarta.inject.Singleton;
@Singleton
public class DefaultGreetingService implements IGreetingService {
@Override
public String getGreeting() {
return "hello, ";
}
}然后在控制器中注入服务:
@Controller("/greet")
public class GreetingController {
private final IGreetingService greetingService;
@Inject
public GreetingController(IGreetingService greetingService) {
this.greetingService = greetingService;
}
@Get("/{name}")
public String greet(String name) {
return greetingService.getGreeting() + name;
}
}
4. 声明式HTTP客户端
Micronaut提供了声明式HTTP客户端,用过 forest 的肯定不陌生,只需添加依赖后定义接口即可:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-http-client-core</artifactId>
</dependency> package com.cxl.service;
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Get;
import io.micronaut.http.client.annotation.Client;
@Client("/greet")
public interface GreetingClient {
@Get("/{name}")
String greet(String name);
}使用客户端:
@Inject
GreetingClient client;
String greeting = client.greet("Micronaut");5. 测试
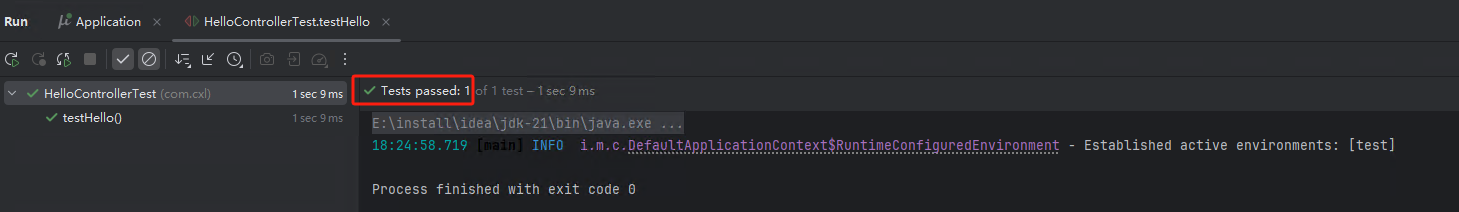
Micronaut强调可测试性,提供了专门的测试注解@MicronautTest:
package com.cxl;
import io.micronaut.http.client.annotation.Client;
import io.micronaut.test.extensions.junit5.annotation.MicronautTest;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import io.micronaut.http.client.HttpClient;
@MicronautTest
public class HelloControllerTest {
@Inject
@Client("/")
HttpClient client;
@Test
void testHello() {
String response = client.toBlocking().retrieve("/hello/chenxianlin");
assert response.equals("Hello chenxianlin");
}
}
数据库访问
Micronaut支持多种数据访问方式,包括JPA、Hibernate、MongoDB等。以下是使用JPA的示例:
添加依赖(Maven):
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.data</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-data-hibernate-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.data</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-data-processor</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.sql</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-jdbc-hikari</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>配置数据源(application.yml):
datasources:
default:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db-type: mysql
dialect: MYSQL
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3366/demo?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: root
jpa:
default:
properties:
hibernate:
hbm2ddl:
auto: update定义实体:
@Serdeable // 序列化,很重要
@Entity
@Table(name = "person")
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String birth;
private String status;
// 省略getter/setter
}创建Repository:
@Repository
public interface PersonRepository extends JpaRepository<Person,Long> {}在服务中使用:
public interface IPersonService {
List<Person> findAll();
Person findById(Long id);
Person save(Person person);
}
@Singleton
public class PersonService implements IPersonService {
@Inject
private PersonRepository personRepository;
@Override
public List<Person> findAll() {
return personRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Person findById(Long id) {
return personRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
@Override
public Person save(Person person) {
return personRepository.save(person);
}
}定义接口:
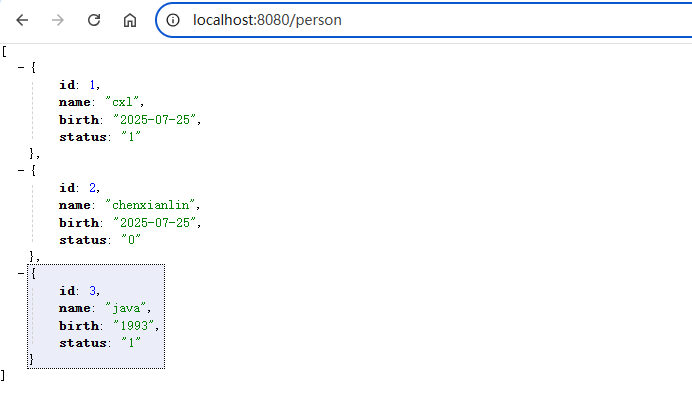
@Controller("/person")
public class PersonController {
@Inject
IPersonService personService;
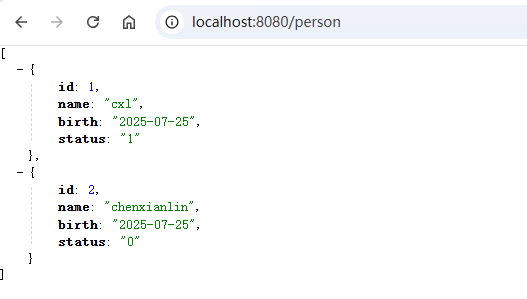
@Get
public List<Person> getPerson() {
return personService.findAll();
}
@Get("/{id}")
public Person getPersonById(Long id) {
return personService.findById(id);
}
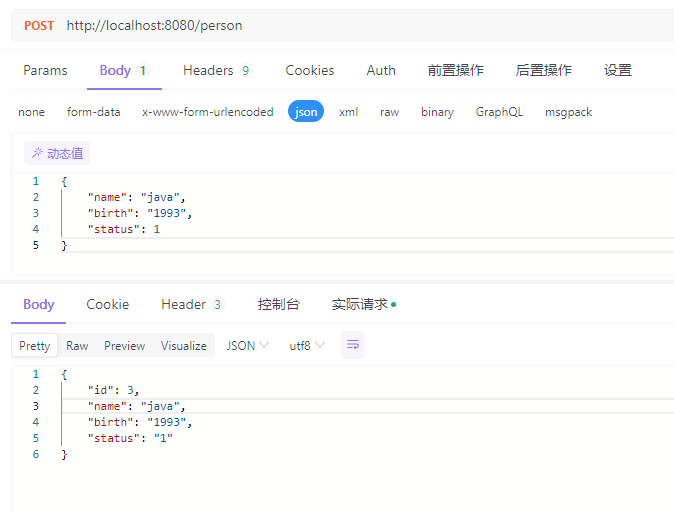
@Consumes("application/json")
@Post
public Person savePerson(@Body Person person) {
return personService.save(person);
}
}
Micronaut最佳实践
基于实际项目经验,以下是使用Micronaut的最佳实践建议:
合理使用作用域:
默认使用
@Prototype作用域(每次注入新实例)对于无状态服务,使用
@Singleton减少对象创建开销
响应式编程选择:
新项目推荐使用Reactor(Mono/Flux)
已有RxJava项目可继续使用Observable/Single
配置管理:
环境相关配置使用
application-{env}.yml敏感信息通过环境变量或Vault注入
测试策略:
充分利用
@MicronautTest加速测试对于简单组件测试,可使用普通单元测试避免启动上下文
GraalVM原生镜像:
从项目开始就考虑原生兼容性
使用
@ReflectiveAccess等注解谨慎处理反射需求逐步测试和调整原生镜像配置
微服务设计:
每个服务保持小而专注
使用Micronaut的
@Client实现类型安全的服务调用实现适当的弹性模式(重试、断路器)